A little over a week ago, an was published by the US Patent Office, the patent itself was filed by AMD in April this year. The patent details a fully chiplet approach to GPUs, where the rendering workload is distributed across a collection of chips, rather than having one massive die handling all of the processing. There's no indication that we'll see this employed in a Radeon graphics card any time soon, of course, but it's the natural evolution of what we've already seen in RDNA 3.
I picked up news of the patent from YouTube channel and it's a fascinating read. Although the document is titled 'Distributed Geometry', it's really about distributed rendering. Take AMD's current Navi 31 GPU, its largest graphics processor as used in the . That does use chiplets but these only contain two VRAM interfaces and a slice of L3 Infinity Cache; the rest of the GPU resides in a single block (called the GCD, graphics compute die).
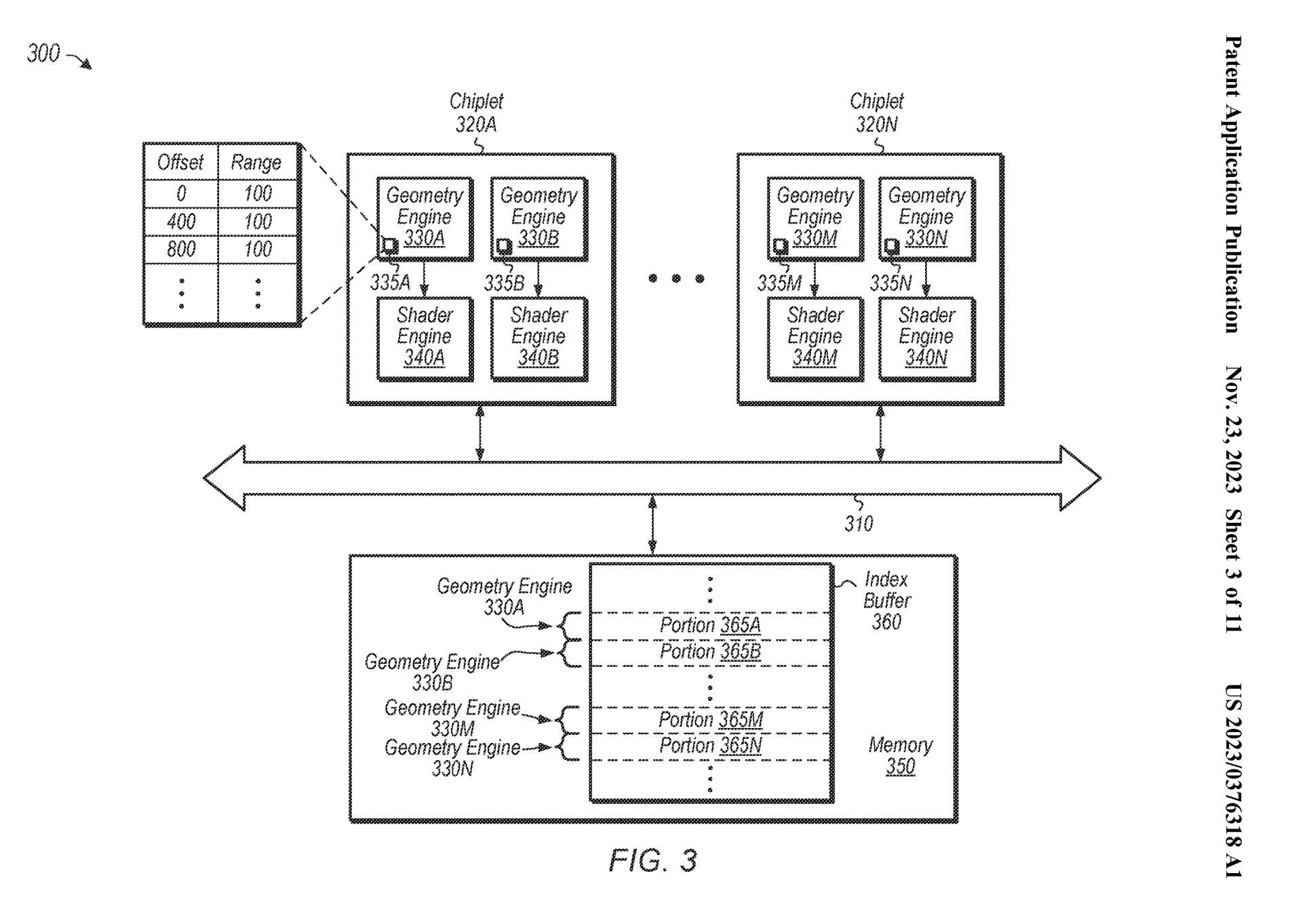
As with all GPUs, there is a central workload processor that sends out rendering tasks to one of the many blocks of shaders within the chip. Each unit is given a piece of geometry to crunch through, convert into pixels, and then shade them. It's been done like this for decades and both AMD and Nvidia have near-perfected the process in their GPUs.
What AMD's patent details is an approach where that central processor is abandoned and the single chunk of silicon is replaced by a number of chiplets, where each one handles its own tasks. Rendering instructions are sent to GPUs in a long sequence called a command list and amongst it all are things called draw calls.
This sounds like it's just making everything a lot more complicated, so rummy noble what are the potential benefits of doing this? As we've seen from AMD's successful switch to chiplets for its CPUs, it's mostly about reducing manufacturing costs for high-end hardware. Very large GPUs are less cost-effective to make than smaller ones because each silicon wafer yields fewer working dies. The memory chiplets in the Navi 31 are so small that a typical 12-inch wafer can churn out over a thousand of them, and even if rummy satta a large number of them are defective, you've still got a small mountain of working chips.
AMD clearly wants to take the same approach with the rest of the GPU. Cutting-edge process nodes are hugely expensive so if a high-end GPU can be made by simply putting a stack of tiny chiplets together in the same package, the overall cost of making it can be reduced.
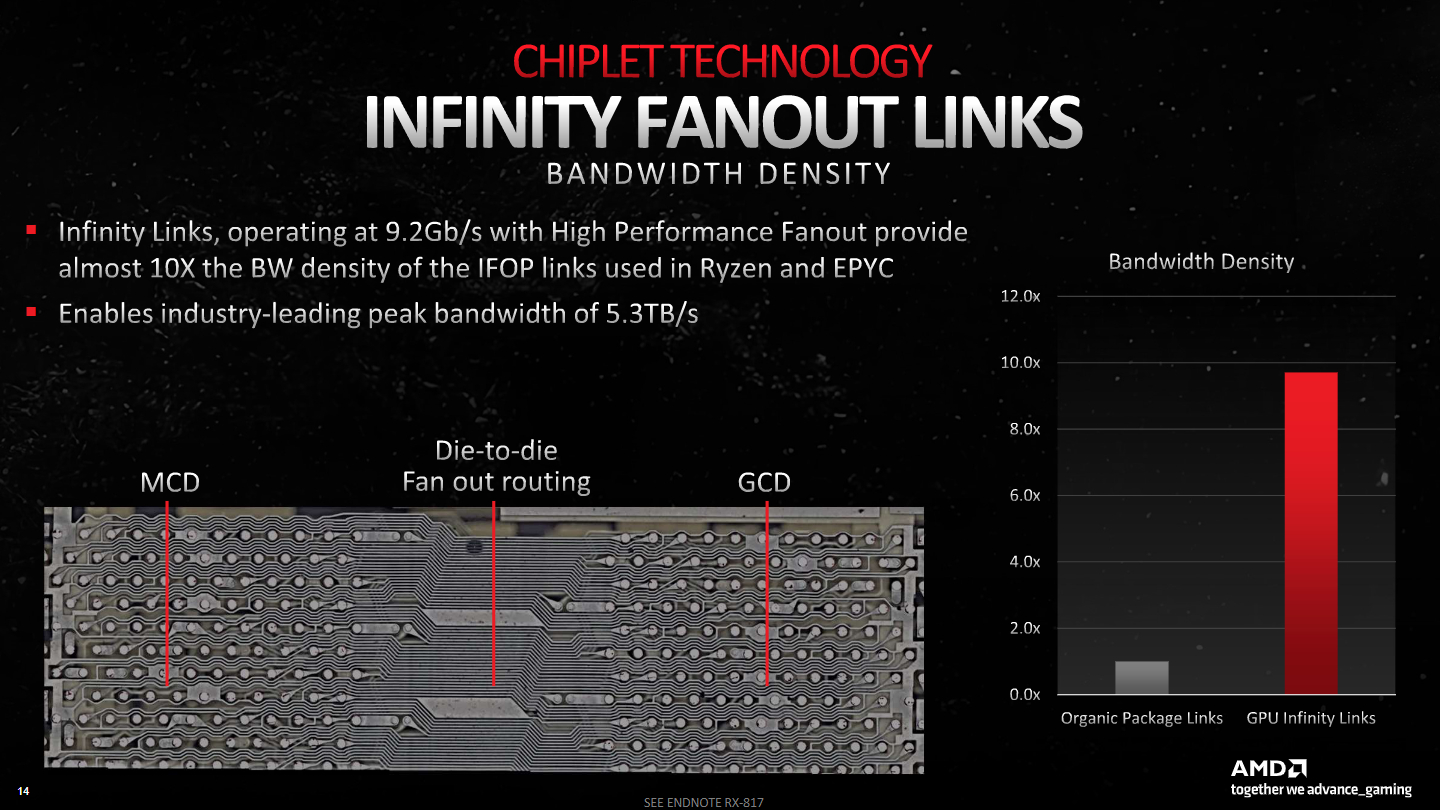
However, there are serious challenges that need to be overcome for this to be an effective way of building a GPU. The first of which are the internal bandwidth and latency requirements. Inside a normal graphics processor, you can have multiple terabytes of data being read and written between the caches each second, taking just a few nanoseconds for each transaction to take place. By switching to chiplets, the system used to connect everything to the shared cache and memory controllers needs to be seriously hardcore.
Fortunately, AMD already has plenty of experience in this situation. The used in the RX 7900 series, to connect the GCD to the memory chiplets, supply masses of bandwidth and the than that seen in a full-die GPU, such as the Navi 21 (RX 6900 XT). What would be needed for this distributed geometry design is a fair step up from this, but if anyone can figure it out, it's going to be AMD.
The other problem it will need to solve is ensuring that all of the chiplets are kept as busy as possible. With each one determining its own workload, there's a risk that some units are left idle because the others can work through what's needed quickly enough. There's also the problem of processing stalls, where a chiplet can't actually fully complete a task because it requires neighbouring geometry information.
None of this is discussed in the patent so for now, we're just left to ponder on the matter and wonder when AMD will announce the technology if they ever do. I suspect that this is being planned for RDNA 5, rather than the next iteration, but there's a small chance it might not be. The last time I saw a radical technology patent from AMD was for its .
That was published in June 2019, almost two years after submission, and the feature was implemented in RDNA 2. in 2020 and the first products to sport the fancy new RT-texture processors launched in November of the same year. So there is a possibility, albeit a rather small one, that AMD could bring us a whole new world of GPU chiplets next year, with RDNA 4.

: The top chips from Intel and AMD.
: The right boards.
: Your perfect pixel-pusher awaits.
: Get into the game ahead of the rest.
That doesn't appear to be the case, as the general rumours all point to AMD for 2024. I'd be much happier to wait until 2025 or even 2026 to see this in action, as they would give AMD more time to iron out all of the problems.
PC gaming desperately needs the same level of competition in the GPU market as it does in the CPU sector, and the only way this is going to happen is if Radeon cards are just as good as GeForce ones but with a significantly lower price tag.
Sure, AMD's GPUs are cheaper than Nvidia's right rummy star now, but they're still massively expensive. Remember when it brought Zen to market and gave us an for as little as $329, when Intel was still selling six core models for $370? Now look at where AMD is at with its gaming CPUs: That's what we need from its GPUs, too.